Indonesia Import Procedure Explained
Indonesia ImportProcedure Explained for any goods coming from overseas into the Indonesian
customs territory are treated as “import” and are generally subject to customs
duty. Indonesia Import Procedure of goods into Indonesia is subject to customs
verification, i.e. verification of documentation and physical inspection of
goods.
Importation of goods
into Indonesia must be declared to the Customs Authority using an Import
Declaration Form (PIB). To be able to fulfill customs obligations, the importer
must register with the DGCE to obtain a Customs Identification Number (NIK). Customs
duty and import taxes payable should be settled first before the goods are
released from the customs area (airports and harbors). If the deadline is not
met, the customs duty payable is subject to an administrative penalty of 10%
from the customs duty payable.
Requirement for Indonesia import procedure
An importer can be a
person or company, whether it has legal entity status or not. An importer must
have a Customs Identification Number (Nomor Identitas Kepabeanan, NIK) and an
Importer Identification Number (Angka Pengenal Impor, API). Importation of
certain products requires the importer to have a Special Importer
Identification Number (Nomor Pengenal Importir Khusus, NPIK) or Registered
Importer Number (Importir Terdaftar Produk Tertentu, ITPT). All importer must
have these license to completing the Indonesia
import procedure
Customs Identification Number (NIK) to completing Indonesia import procedure
NIK must be obtained
from the DGCE and will remain valid unless it is cancelled by the DGCE.
Importer Identification Number (API)
All importers must have
an API. Currently there are two types of API as summarized in the table below:
The API is valid for
five years and can be extended. It is applicable for the entire Indonesian
customs territory.
Starting January 2011,
API-P holders may also import finished goods to support their business
activities, subject to certain criteria or requirements.
Importation without an
API can only be done after obtaining approval from the Indonesian Minister of
Trade (MoT) and only for infrequent importation of self-consumed goods (not for
trading purposes).
Special Importer Identity Number (NPIK) other requirement for Indonesia
import procedure
NPIK should be obtained
by companies that import certain commodities such as rice, electronic products,
sugar, corn, soybeans, toys, footwear, and textiles. The NPIK can be obtained
from the Ministry of Trade by an importer that already has an API, and is valid
for five years.
An importer that holds
an NPIK should file a written report regarding its import realization to the
Ministry of Trade on.the 15th of every month.
Registered Importer Number (ITPT) other requirements for Indonesia
import procedure
Certain products can only
be imported by a Registered Importer of Certain Products (Importir Terdaftar
Produk Tertentu, ITPT). The current list of certain products that can only be
imported by ITPT is as follows:
-
electronic products;
-
ready-made garments
-
toys
-
footwear
-
food and drink products
-
cosmetic products; and
-
traditional and herbal medicines
Customs Declaration Forms
1.
The Importer must prepare a Customs Declaration
Form (PIB) upon the importation of goods.
2.
The customs declaration should be accompanied by
supporting documents, i.e. commercial invoice, airway bill (AWB) or bill of
lading (B/L), packing list (P/L), insurance letter, etc.
3.
Revision of an import declaration can be done
under certain circumstances. Revision can be made to an import declaration,
provided the imported goods have not been released from the temporary customs
area, the error was not discovered by the customs officials, and no assessment
has been issued.
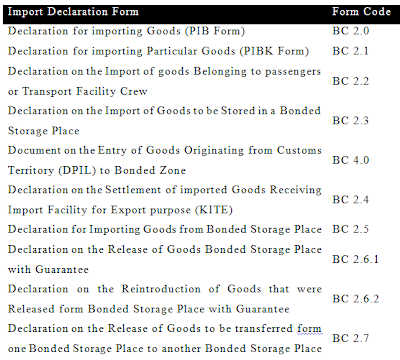
4.
The type of import declaration form depends on
the purpose of the importation, as follows:
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
General Procedure of Importation
The procedures of importation are as follows:
1.
Arrival of transportation vehicle (ship,
airplane, etc.)
Before
the arrival of a transportation vehicle from outside the customs territory, the
carrier must notify the Customs Office of the planned arrival of the vehicle.
2.
Arrival of Import Goods
Upon
the vehicle's arrival, the carrier must submit a customs declaration, i.e.
manifest, to the Head of the Customs Office within 24 hours after the arrival
of the ship (eight hours for aircraft; immediately for land transport), in Indonesian
or English, signed by the carrier.
3.
Discharge of Import Goods
The
import goods shall be discharged at the customs area or other place after
receiving approval from the Head of Investigation or authorized officer. The
carrier shall provide a list of the containers or break bulk amount which has
been discharged to the authorized officer at the Customs Office, either
manually or electronically, this is part of Indonesia import procedure
4. Procedure
for Clearance / Release of Import Goods from Customs Area.
-
The importer shall complete and submit the PIB,
compute the customs duty and import taxes, and make payment to the depository
bank;
-
The PIB and its attachments, such as commercial
invoice, P/L, B/L / AWB, customs duty and import taxes payment evidence, etc.,
are submitted to the Customs Authority for approval;
-
The import goods can be released from the
customs area after approval by the Customs Authority.
5.
Computation of Customs duty and import taxes
- Customs Duty = Customs duty tariff x CIF Value
(Cost, Insurance and Freight) If the insurance and freight are unknown, the
DGCE provides guidance to calculate the deemed amount based on a percentage.
-
Value Added Tax = 10% x [CIF Value plus customs
duty]
-
Article 22 Income Tax = Tariff x [CIF plus
customs duty]
-
The tariff of article 22 income tax is 2.5% for
API holder and 7.5% for non-API holder.
-
Luxury Goods Sales Tax (LGST) = Tariff x [CIF
Value plus customs duty] LGST is only imposed on certain goods that are defined
as luxury goods.
All above explanations are some
requirements of Indonesia import procedure.